从WordCount开始
下面是一个使用flink进行word出现次数统计的示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataStream<String> text = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 8080);
DataStream<WordWithCount> windowCounts =
text.flatMap(
(FlatMapFunction<String, WordWithCount>)
(value, out) -> {
for (String word : value.split(",")) {
out.collect(new WordWithCount(word, 1L));
}
},
Types.POJO(WordWithCount.class))
.keyBy(value -> value.word)
.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5)))
.reduce((a, b) -> new WordWithCount(a.word, a.count + b.count))
.returns(WordWithCount.class);
// 设置并发度,单并发打印输出结果
windowCounts.print().setParallelism(1);
env.execute("Socket Window WordCount");
}
public static class WordWithCount {
public String word;
public long count;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public WordWithCount() {}
public WordWithCount(String word, long count) {
this.word = word;
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// print底层会调用toString进行输出
// stream.println(completedPrefix + record.toString());
return word + " : " + count;
}
}
|
通过nc命令进行数据输入
1
2
|
# nc -lk 8080
a,b,c,b,c,d,c,d
|
运行程序后,可以看到输出结果如下:
1
2
3
4
|
c : 3
b : 2
a : 1
d : 2
|
在上面代码中,socketTextStream、flatMap等算子会转换成一系列的Transformation,当然并不是所有的算子都有对应的Transformation转换,比如window算子,它仅仅是作为上下游算子的桥梁,本身不会转换成相应的Transformation。
而这些Transformation之间通过不同算子的组合,组成一个Transformation依赖链,上游算子作为下游算子的input,最终这个依赖关系以链表的形式存储在StreamExecutionEnvironment中
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class StreamExecutionEnvironment implements AutoCloseable {
...
// 存储Transformation列表
protected final List<Transformation<?>> transformations = new ArrayList<>();
...
}
|
在构建Transformation依赖链时,有的算子会生成对应的StreamOperator,比如上面的flatMap对应的userFunction就是存储在对应的operator中的,我们从后面的分析也可以知道,这些具备userFunction的算子最终都会转换成StreamGraph中的StreamNode节点,后面会有介绍。
在分析Transformation链表生成过程时,我们需要更关注每一个算子背后所对应的Transformation类型以及其对应的StreamOperator(如果存在)类型。
socketTextStream算子会返回DataStreamSource,并绑定一个初始的LegacySourceTransformation,其对应的StreamOperator类型为StreamSource。为了查看其依赖关系的变化,这里继续跟进flatMap算子
flatMap
1
2
3
4
5
|
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> flatMap(
FlatMapFunction<T, R> flatMapper, TypeInformation<R> outputType) {
// 这里会生成StreamOperator对象,类型为StreamFlatMap
return transform("Flat Map", outputType, new StreamFlatMap<>(clean(flatMapper)));
}
|
继续transform
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
protected <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> doTransform(
String operatorName,
TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
StreamOperatorFactory<R> operatorFactory) {
// read the output type of the input Transform to coax out errors about MissingTypeInfo
transformation.getOutputType();
// 生成flatMap对应的Transformation,并将上游的this.transformation作为其input输入
OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform =
new OneInputTransformation<>(
this.transformation,
operatorName,
operatorFactory,
outTypeInfo,
// 设置Transformation的并发度
environment.getParallelism());
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> returnStream =
new SingleOutputStreamOperator(environment, resultTransform);
// 加入到StreamExecutionEnvironment的transformations链表中
getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform);
return returnStream;
}
|
在flatMap算子中,会返回SingleOutputStreamOperator类型,包括上面socketTextStream返回的DataStreamSource类型,这些都是DataStream类型的子类,通过这些类型的method调用,可以串联起各个算子的依赖关系。
window
上面的flatMap等其他算子在内部都会有对应的Transformation对象,而window算子并没有这个对应关系,window算子只是作为其上游算子和下游算子的中间桥梁,用于构建其上下游算子的依赖关系,并传入一些用户配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public <W extends Window> WindowedStream<T, KEY, W> window(
WindowAssigner<? super T, W> assigner) {
return new WindowedStream<>(this, assigner);
}
public WindowedStream(KeyedStream<T, K> input, WindowAssigner<? super T, W> windowAssigner) {
// 上游的keyedStream作为其输入
this.input = input;
this.builder =
new WindowOperatorBuilder<>(
// 用户传入的WindowAssigner对象
windowAssigner,
windowAssigner.getDefaultTrigger(input.getExecutionEnvironment()),
input.getExecutionConfig(),
input.getType(),
input.getKeySelector(),
input.getKeyType());
}
|
从上面的代码也可以看出,window并没有对应的Transformation,仅仅是构造了一个WindowedStream对象。由于下游算子是reduce,因此我们继续查看该WindowedStream对象的reduce方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> reduce(
ReduceFunction<T> reduceFunction,
WindowFunction<T, R, K, W> function,
TypeInformation<R> resultType) {
// clean the closures
function = input.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(function);
reduceFunction = input.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(reduceFunction);
final String opName = builder.generateOperatorName();
final String opDescription = builder.generateOperatorDescription(reduceFunction, function);
// 生成StreamOperator对象,
// 根据是否有设置window相关的Evictor,分别返回WindowOperator或者EvictingWindowOperator类型
OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator = builder.reduce(reduceFunction, function);
// 调用KeyedStream的doTransform方法,和flatMap类似,即生成Transformation并加入到transformations列表
return input.transform(opName, resultType, operator).setDescription(opDescription);
}
|
通过上面的分析,可以比较容易的看到各个Transformation的依赖变化情况,这里列出完整算子的依赖关系图,不再具体分析每一个算子,如下所示:
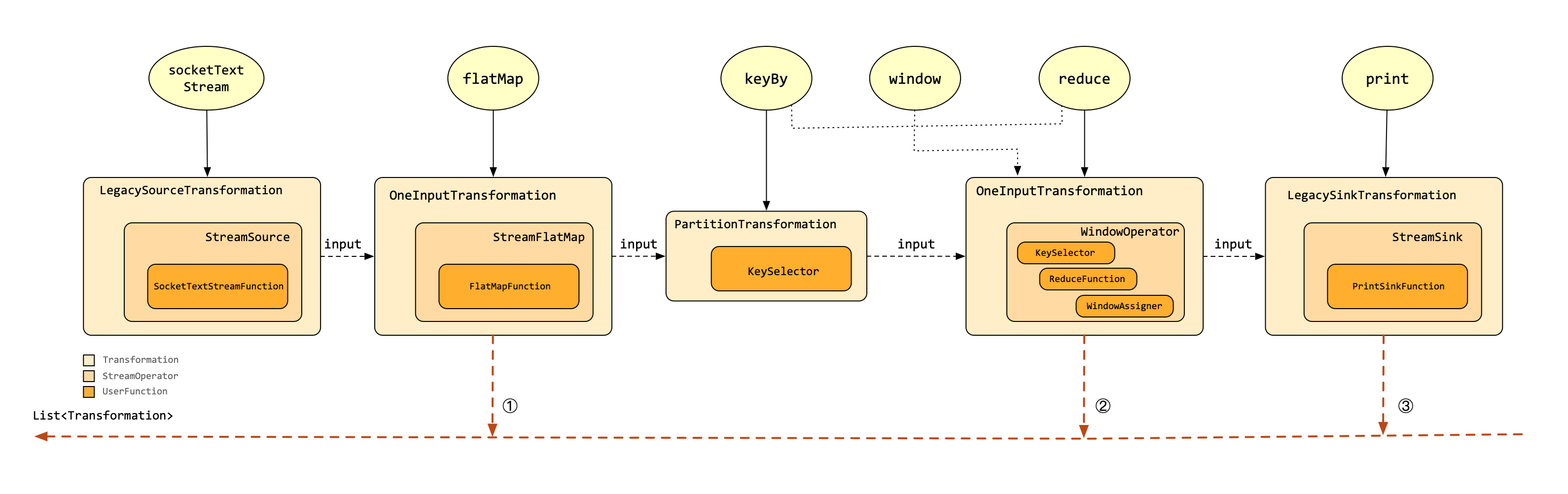
在上面图中,展现出来StreamOperator和Transformation与其相应的算子之间的对应关系,示例中共有3个Transformation实例加入到Transformation链表中。
生成StreamGraph
在构建完Transformation依赖链之后,会继续生成StreamGraph,其具体的生成逻辑代码在StreamGraphGenerator.generate中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public StreamGraph generate() {
streamGraph = new StreamGraph(executionConfig, checkpointConfig, savepointRestoreSettings);
// 默认情况,只有全部任务running才会进行checkpoint,可以设置有finished task时也进行checkpoint
streamGraph.setEnableCheckpointsAfterTasksFinish(
configuration.get(
ExecutionCheckpointingOptions.ENABLE_CHECKPOINTS_AFTER_TASKS_FINISH));
shouldExecuteInBatchMode = shouldExecuteInBatchMode();
// 设置基本配置,包括jobType、状态后端,checkpoint等
configureStreamGraph(streamGraph);
// 底层可能会递归遍历,这里记录已经转换的Transformation避免重复transform
alreadyTransformed = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// 遍历Transformation进行转换
for (Transformation<?> transformation : transformations) {
transform(transformation);
}
// slotSharingGroup信息
streamGraph.setSlotSharingGroupResource(slotSharingGroupResources);
setFineGrainedGlobalStreamExchangeMode(streamGraph);
// 设置是否进行UnalignedCheckpoints
for (StreamNode node : streamGraph.getStreamNodes()) {
if (node.getInEdges().stream().anyMatch(this::shouldDisableUnalignedCheckpointing)) {
for (StreamEdge edge : node.getInEdges()) {
edge.setSupportsUnalignedCheckpoints(false);
}
}
}
final StreamGraph builtStreamGraph = streamGraph;
alreadyTransformed.clear();
alreadyTransformed = null;
streamGraph = null;
return builtStreamGraph;
}
|
在transform中,会根据不同的Transformation类型获取对应的TransformationTranslator,然后通过其继续进行translate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
final TransformationTranslator<?, Transformation<?>> translator =
(TransformationTranslator<?, Transformation<?>>)
translatorMap.get(transform.getClass());
Collection<Integer> transformedIds;
if (translator != null) {
transformedIds = translate(translator, transform);
} else {
transformedIds = legacyTransform(transform);
}
|
在translate代码中对每个Transformation的input进行递归调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
private Collection<Integer> translate(
final TransformationTranslator<?, Transformation<?>> translator,
final Transformation<?> transform) {
checkNotNull(translator);
checkNotNull(transform);
// 递归调用Transformation对应的input Transformation
final List<Collection<Integer>> allInputIds = getParentInputIds(transform.getInputs());
// 避免重复translate
if (alreadyTransformed.containsKey(transform)) {
return alreadyTransformed.get(transform);
}
// 计算slotSharingGroup
// 1. Transformation是否设置slotSharingGroup
// 2. 其inputs是否设置且所有inputs设置相同
// 3. 否则返回default
final String slotSharingGroup =
determineSlotSharingGroup(
transform.getSlotSharingGroup().isPresent()
? transform.getSlotSharingGroup().get().getName()
: null,
allInputIds.stream()
.flatMap(Collection::stream)
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
final TransformationTranslator.Context context =
new ContextImpl(this, streamGraph, slotSharingGroup, configuration);
// 调用TransformationTranslator继续转换
return shouldExecuteInBatchMode
? translator.translateForBatch(transform, context)
: translator.translateForStreaming(transform, context);
}
|
生成StreamNode
从上面的Transformation依赖链生成过程知道,其中flatMap对应返回OneInputTransformation类型,其对应的translator为OneInputTransformationTranslator,这里仍旧以此为例,具体的translate代码位于AbstractOneInputTransformationTranslator中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
protected Collection<Integer> translateInternal(
final Transformation<OUT> transformation,
final StreamOperatorFactory<OUT> operatorFactory,
final TypeInformation<IN> inputType,
@Nullable final KeySelector<IN, ?> stateKeySelector,
@Nullable final TypeInformation<?> stateKeyType,
final Context context) {
final StreamGraph streamGraph = context.getStreamGraph();
final String slotSharingGroup = context.getSlotSharingGroup();
final int transformationId = transformation.getId();
final ExecutionConfig executionConfig = streamGraph.getExecutionConfig();
// 添加StreamNode节点
streamGraph.addOperator(
transformationId,
slotSharingGroup,
transformation.getCoLocationGroupKey(),
operatorFactory,
inputType,
transformation.getOutputType(),
transformation.getName());
if (stateKeySelector != null) {
// 如果跟进之前的示例代码,会发现针对reduce算子,KeyedStream实例在生成Transformation时候
// 会设置其stateKeySelector等信息,参考KeyedStream.doTransform方法
TypeSerializer<?> keySerializer = stateKeyType.createSerializer(executionConfig);
streamGraph.setOneInputStateKey(transformationId, stateKeySelector, keySerializer);
}
// 设置并发度
int parallelism =
transformation.getParallelism() != ExecutionConfig.PARALLELISM_DEFAULT
? transformation.getParallelism()
: executionConfig.getParallelism();
streamGraph.setParallelism(transformationId, parallelism);
streamGraph.setMaxParallelism(transformationId, transformation.getMaxParallelism());
final List<Transformation<?>> parentTransformations = transformation.getInputs();
// OneInputTransformation只有一个input
checkState(
parentTransformations.size() == 1,
"Expected exactly one input transformation but found "
+ parentTransformations.size());
// 添加StreamEdge
for (Integer inputId : context.getStreamNodeIds(parentTransformations.get(0))) {
streamGraph.addEdge(inputId, transformationId, 0);
}
return Collections.singleton(transformationId);
}
|
在streamGraph.addOperator中会根据StreamOperatorFactory类型,决定StreamTask类型,而这个类型也就是作业执行过程中,真正的Task实例类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public <IN, OUT> void addOperator(
Integer vertexID,
@Nullable String slotSharingGroup,
@Nullable String coLocationGroup,
StreamOperatorFactory<OUT> operatorFactory,
TypeInformation<IN> inTypeInfo,
TypeInformation<OUT> outTypeInfo,
String operatorName) {
// 示例中的所有StreamOperatorFactory均为SimpleOperatorFactory,对应的class为OneInputStreamTask
Class<? extends TaskInvokable> invokableClass =
operatorFactory.isStreamSource()
? SourceStreamTask.class
: OneInputStreamTask.class;
addOperator(
vertexID,
slotSharingGroup,
coLocationGroup,
operatorFactory,
inTypeInfo,
outTypeInfo,
operatorName,
invokableClass);
}
|
生成StreamEdge
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
private void addEdgeInternal(
Integer upStreamVertexID,
Integer downStreamVertexID,
int typeNumber,
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner,
List<String> outputNames,
OutputTag outputTag,
StreamExchangeMode exchangeMode,
IntermediateDataSetID intermediateDataSetId) {
// 比如在使用sideOutputLateData时,通过SingleOutputStreamOperator.getSideOutput(OutputTag)时,
// 会在上下游算子之间创建SideOutputTransformation,而SideOutputTransformation的转换结果就会创建一个virtualNode
if (virtualSideOutputNodes.containsKey(upStreamVertexID)) {
int virtualId = upStreamVertexID;
// 针对虚拟节点,会递归查找其上游的非虚拟节点,然后创建StreamEdge
upStreamVertexID = virtualSideOutputNodes.get(virtualId).f0;
if (outputTag == null) {
outputTag = virtualSideOutputNodes.get(virtualId).f1;
}
addEdgeInternal(
upStreamVertexID,
downStreamVertexID,
typeNumber,
partitioner,
null,
outputTag,
exchangeMode,
intermediateDataSetId);
} else if (virtualPartitionNodes.containsKey(upStreamVertexID)) {
// 比如之前的keyBy所创建的PartitionTransformation就会创建对应的virtualNode
int virtualId = upStreamVertexID;
upStreamVertexID = virtualPartitionNodes.get(virtualId).f0;
if (partitioner == null) {
partitioner = virtualPartitionNodes.get(virtualId).f1;
}
exchangeMode = virtualPartitionNodes.get(virtualId).f2;
addEdgeInternal(
upStreamVertexID,
downStreamVertexID,
typeNumber,
partitioner,
outputNames,
outputTag,
exchangeMode,
intermediateDataSetId);
} else {
createActualEdge(
upStreamVertexID,
downStreamVertexID,
typeNumber,
partitioner,
outputTag,
exchangeMode,
intermediateDataSetId);
}
}
|
在createActualEdge中,针对上下游的StreamNode,如果不存在StreamPartitioner,则会根据相应的配置新建一个StreamPartitioner,用于控制上下游的数据balance策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
private void createActualEdge(
Integer upStreamVertexID,
Integer downStreamVertexID,
int typeNumber,
StreamPartitioner<?> partitioner,
OutputTag outputTag,
StreamExchangeMode exchangeMode,
IntermediateDataSetID intermediateDataSetId) {
StreamNode upstreamNode = getStreamNode(upStreamVertexID);
StreamNode downstreamNode = getStreamNode(downStreamVertexID);
if (partitioner == null
&& upstreamNode.getParallelism() == downstreamNode.getParallelism()) {
partitioner =
executionConfig.isDynamicGraph()
? new ForwardForUnspecifiedPartitioner<>()
: new ForwardPartitioner<>();
} else if (partitioner == null) {
partitioner = new RebalancePartitioner<Object>();
}
...
}
|
生成框图
综上所述,由Transformation生成StreamGraph的大致框图如下所示:
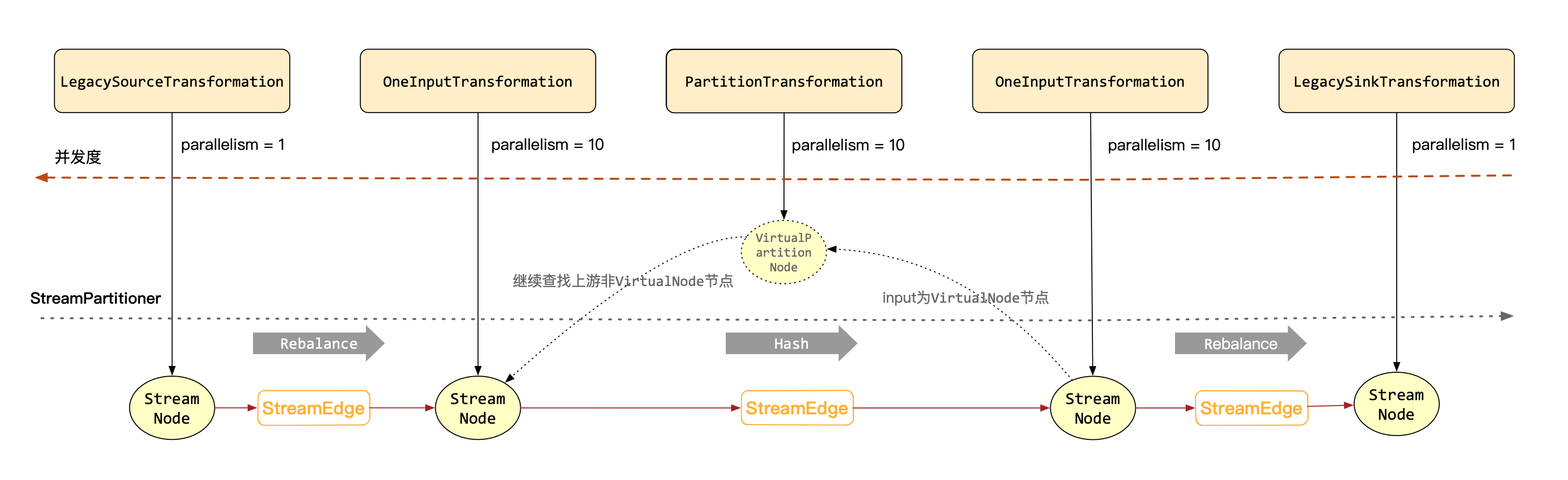
另外,在生成完StreamGraph之后,我们同样可以通过streamGraph.getStreamingPlanAsJSON()方法打印出其json格式数据以便查看
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
{
"nodes" : [ {
"id" : 1,
"type" : "Source: Socket Stream",
"pact" : "Data Source",
"contents" : "Source: Socket Stream",
"parallelism" : 1
}, {
"id" : 2,
"type" : "Flat Map",
"pact" : "Operator",
"contents" : "Flat Map",
"parallelism" : 10,
"predecessors" : [ {
"id" : 1,
"ship_strategy" : "REBALANCE",
"side" : "second"
} ]
}, {
"id" : 4,
"type" : "TumblingProcessingTimeWindows",
"pact" : "Operator",
"contents" : "Window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows(5000), ProcessingTimeTrigger, WordCountDemo$$Lambda$112/1311146128, PassThroughWindowFunction)",
"parallelism" : 10,
"predecessors" : [ {
"id" : 2,
"ship_strategy" : "HASH",
"side" : "second"
} ]
}, {
"id" : 5,
"type" : "Sink: Print to Std. Out",
"pact" : "Data Sink",
"contents" : "Sink: Print to Std. Out",
"parallelism" : 1,
"predecessors" : [ {
"id" : 4,
"ship_strategy" : "REBALANCE",
"side" : "second"
} ]
} ]
}
|
上面的json结果可以使用flink提供的visualizer图形化工具进行可视化查看
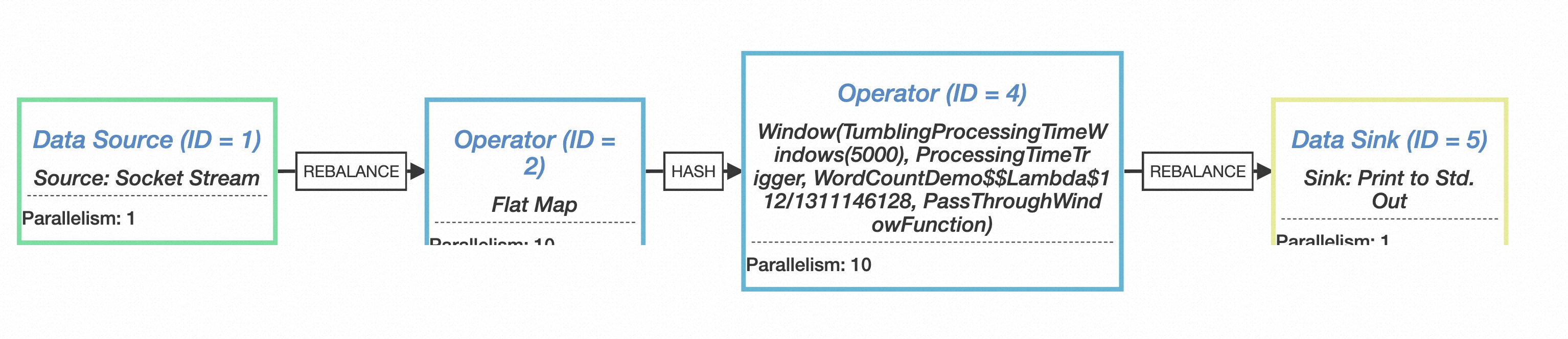
并发度
在生成StreamNode的时候会有并发度parallelism的设置,对应上面json中的数值,这里也可以看下并发度的设置逻辑
socketTextStream
在addSource的时候会根据SourceFunction的类型设置并发度
1
2
3
4
|
boolean isParallel = function instanceof ParallelSourceFunction;
if (!isParallel) {
setParallelism(1);
}
|
flatMap
在flatMap算子中,DataStream进行doTransform的时候,会设置为environment.getParallelism()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform =
new OneInputTransformation<>(
this.transformation,
operatorName,
operatorFactory,
outTypeInfo,
environment.getParallelism());
|
environment.getParallelism
而environment的默认并发度设置则是在获取env的时候,以LocalStreamEnvironment 为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// 获取env实例
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// 创建LocalStreamEnvironment
public static LocalStreamEnvironment createLocalEnvironment(Configuration configuration) {
if (configuration.getOptional(CoreOptions.DEFAULT_PARALLELISM).isPresent()) {
return new LocalStreamEnvironment(configuration);
} else {
Configuration copyOfConfiguration = new Configuration();
copyOfConfiguration.addAll(configuration);
copyOfConfiguration.set(CoreOptions.DEFAULT_PARALLELISM, defaultLocalParallelism);
return new LocalStreamEnvironment(copyOfConfiguration);
}
}
// 而defaultLocalParallelism默认值则是依据CPU核数来确认的
private static int defaultLocalParallelism = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
|
print
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// print会返回DataStreamSink,调用其setParallelism也可以设置并发度
windowCounts.print().setParallelism(1);
public DataStreamSink<T> setParallelism(int parallelism) {
transformation.setParallelism(parallelism);
return this;
}
|


